Jeep Cherokee (XJ): Cleaning and inspection
Thoroughly clean all the governor parts in a suitable
cleaning solution but do not use any type of
caustic cleaning agents.
The governor weight components (Fig. 218) and the
governor valve (Fig. 219), must slide freely in their
bores when clean and dry. Minor surface scratches
and burrs can be smoothed with crocus cloth.
The aluminum governor valve and outer weight
have a hard coating on them. Check condition of this
coating carefully. Do not reuse either part if the coating
is damaged.
Inspect the governor weight spring for distortion.
Replace the spring, if distorted, collapsed, or broken.
Clean the filter in solvent and dry it with compressed
air. Replace the filter, if damaged. Inspect the park
gear for chipped or worn gear teeth or damaged ring
grooves. Replace the gear, if damaged.
Check the teeth on the park gear for wear or damage.
Replace the gear if necessary. Inspect the metal
seal rings on the park gear hub. Replace the rings
only if severely worn, or broken. Clean the housing and park lock components in
solvent and dry them with compressed air.
Examine the park lock components in the housing.
If replacement is necessary, remove the shaft with
parallel jaw snap ring pliers (Fig. 220) and remove
the sprag and spring. Then remove the spring clip
and reaction plug (Fig. 221). Compress the reaction
plug spring clip only enough to remove
and install it. Do not distort the clip during
removal or installation.
Be sure a replacement sprag is installed so the
sprag locking lug will face the park gear (Fig. 222).
Also be sure the spring is correctly positioned as
shown (Fig. 222). The sprag may not retract if the
spring is improperly installed. Serviceable valve body components are: The remaining valve body components are serviced
only as part of a complete valve body assembly.
1 - INTERMEDIATE WEIGHT
1 - SEAL RING (PLAIN END) Clean the valve body components in a parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or
any type of caustic solution. Dry the parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and
free from obstructions.
NOTE: Do not use rags or shop towels to wipe off
valve body components. Lint from these materials
will adhere to the valve body components. Lint will
interfere with valve operation and may clog filters
and fluid passages.
Inspect the throttle and manual valve levers and
shafts. Do not attempt to straighten a bent shaft or
correct a loose lever. Replace these components if
worn, bent, loose or damaged in any way.
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straightedge
to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.
Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with crocus
cloth. The cloth should be in sheet form and be
positioned on a surface plate, sheet of plate glass, or
equally flat surface. However, if distortion is severe
or any surfaces are heavily scored, the valve body
will have to be replaced.
CAUTION: Many of the valve body valves and plugs
are made of coated aluminum. Aluminum components
can be identified by the dark color of the special
coating applied to the surface (or by testing
with a magnet). DO NOT polish or sand aluminum
valves or plugs with any type of material, or under
any circumstances. This practice might damage the
special coating and cause the valves and plugs to
stick and bind.
1 - SPRAG SHAFT
1 - SPRING CLIP
1 - SPRAG SHAFT Inspect the valves and plugs for scratches, burrs,
nicks, or scores. Also inspect the coating on the aluminum
valves and plugs (Fig. 223). If the coating is
damaged or worn through, the valve (or valve body)
should be replaced.
Aluminum valves and plugs should not be sanded
or polished under any circumstances. However, minor
burrs or scratches on steel valves and plugs can be
removed with crocus cloth but do not round off the
valve or plug edges. Squareness of these edges is
vitally important. These edges prevent foreign matter
from lodging between the valves, plugs and bore.
Inspect all the valve and plug bores in the valve
body. Use a penlight to view the bore interiors.
Replace the valve body if any bores are distorted or
scored. Inspect all of the valve body springs. The
springs must be free of distortion, warpage or broken
coils.
Trial fit each valve and plug in its bore to check
freedom of operation. When clean and dry, the valves
and plugs should drop freely into the bores. Valve
body bores do not change dimensionally with use. If
the valve body functioned correctly when new, it will
continue to operate properly after cleaning and
inspection. It should not be necessary to replace a
valve body assembly unless it is damaged in handling.
1 - GOVERNOR PLUG END PLATE Clean the case in a solvent tank. Flush the case
bores and fluid passages thoroughly with solvent.
Dry the case and all fluid passages with compressed
air. Be sure all solvent is removed from the case and
that all fluid passages are clear.
NOTE: Do not use shop towels or rags to dry the
case (or any other transmission component) unless
they are made from lint-free materials. Lint will
readily adhere to case surfaces and transmission
components and will circulate throughout the transmission
after assembly. A sufficient quantity of lint
can block fluid passages and interfere with valve
body operation.
Inspect the case for cracks, porous spots, worn
servo bores, or damaged threads. However, the case
will have to be replaced if it exhibits damage or wear.
Lubricate the front band adjusting screw and locknut
with petroleum jelly and thread it part way into
the case. Be sure the screw turns freely and does not
bind. Install the locknut on the screw after checking
screw thread operation.
Inspect all the transmission bushings during overhaul.
Bushing condition is important as worn, scored
bushings contribute to low pressures, clutch slip and
accelerated wear of other components. Replace worn,
or scored bushings, or if doubt exists about bushing
condition.
Use recommended tools to replace bushings. The
tools are sized and designed to remove, install and
seat bushings correctly. The bushing replacement tools are included in Bushing
Tool Sets C-3887-B, or
C-3887-J.
Pre-sized service bushings are available for
replacement purposes. Only the sun gear bushings
are not serviced. Replace the gear as an assembly if
the bushings are severely scored, or worn.
Heli-Coil inserts are recommended for repairing
damaged, stripped or worn threads in aluminum
parts. Stainless steel inserts are preferred.
The use of crocus cloth is permissible where necessary,
providing it is used carefully. When used on
valves, use extreme care to avoid rounding off sharp
edges. Sharp edges are vital as they prevent foreign
matter from getting between the valve and valve
bore.
Do not reuse oil seals, gaskets, seal rings, or
O-rings during overhaul. Replace these parts as a
matter of course. Also do not reuse snap rings or
E-clips that are bent or distorted. Replace these parts
as well.
Lubricate transmission parts with Mopart ATF
Plus 3, Type 7176 transmission fluid during assembly.
Use Mopart Door Ease, or Ru-Glyde to lubricate
piston seals and O-rings. Use petroleum jelly on
thrust washers and to hold parts in place during
reassembly. Clean the overrunning clutch assembly, clutch cam,
low-reverse drum, and overdrive piston retainer in
solvent. Dry them with compressed air after cleaning.
Inspect condition of each clutch part after cleaning.
Replace the overrunning clutch roller and spring
assembly if any rollers or springs are worn or damaged,
or if the roller cage is distorted, or damaged.
Replace the cam if worn, cracked or damaged.
Replace the low-reverse drum if the clutch race,
roller surface or inside diameter is scored, worn or
damaged. Do not remove the clutch race from
the low-reverse drum under any circumstances.
Replace the drum and race as an assembly if
either component is damaged.
Examine the overdrive piston retainer carefully for
wear, cracks, scoring or other damage. Be sure the
retainer hub is a snug fit in the case and drum.
Replace the retainer if worn or damaged. Clean the servo piston components with solvent
and dry them with compressed air. Wipe the band
clean with lint free shop towels.
Replace the front band if distorted, lining is
burned, flaking off, or worn to the point where the
grooves in the lining material are no longer visible.
Inspect the servo components (Fig. 224). Replace
the springs if collapsed, distorted or broken. Replace
the guide, rod and piston if cracked, bent, or worn.
Discard the servo snap ring if distorted or warped.
Check the servo piston bore for wear. If the bore is
severely scored, or damaged, it will be necessary to
replace the case.
Replace any servo component if doubt exists about
condition. Do not reuse suspect parts. 1 - PISTON RINGS Rear servo Remove and discard the servo piston seal ring (Fig.
225). Then clean the servo components with solvent
and dry with compressed air. Replace either spring if
collapsed, distorted or broken. Replace the plug and
piston if cracked, bent, or worn. Discard the servo
snap rings and use a new ones at assembly. (1) Clean pump and support components with solvent
and dry them with compressed air.
(2) Check condition of the seal rings and thrust
washer on the reaction shaft support. The seal rings
do not need to be replaced unless cracked, broken, or
severely worn.
(3) Inspect the pump and support components.
Replace the pump or support if the seal ring grooves
or machined surfaces are worn, scored, pitted, or
damaged. Replace the pump gears if pitted, worn
chipped, or damaged.
1 - SNAP RING shaft support bushing. Replace either bushing
only if heavily worn, scored or damaged. It is not
necessary to replace the bushings unless they are
actually damaged.
(5) Install the gears in the pump body and measure
pump component clearances as follows:
(a) Clearance between outer gear and reaction
shaft housing should be 0.010 to 0.063 mm (0.0004
to 0.0025 in.). Clearance between inner gear and
reaction shaft housing should be 0.010 to 0.063
mm (0.0004 to 0.0025 in.). Both clearances can be
measured at the same time by:
(I) Installing the pump gears in the pump
housing.
(II) Position an appropriate piece of Plastigagey
across both gears.
(III) Align the plastigage to a flat area on the
reaction shaft housing.
(IV) Install the reaction shaft to the pump
housing.
(V) Separate the reaction shaft housing from
the pump housing and measure the Plastigagey
following the instructions supplied with it.
(b) Clearance between inner gear tooth and
outer gear should be 0.08 to 0.19 mm (0.0035 to
0.0075 in.). Measure clearance with an appropriate
feeler gauge.
(c) Clearance between outer gear and pump
housing should also be 0.010 to 0.19 mm (0.0035 to
0.0075 in.). Measure clearance with an appropriate
feeler gauge. Clean and inspect the front clutch components.
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned or charred, or if the facing is flaking off.
Replace the steel plates if heavily scored, warped, or
broken. Be sure the driving lugs on the plates are in
good condition. The lugs must not be bent, cracked or
damaged in any way.
Replace the clutch spring and spring retainer if
either is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
steel plates should slide freely in the slots. Replace
the retainer if the grooves are worn or damaged.
Check action of the check ball in the retainer (Fig.
226). The ball must move freely and not stick.
NOTE: Inspect the clutch retainer bushings carefully
(Fig. 227). The retainer bushings are NOT serviceable.
It will be necessary to replace the retainer
if either bushing is scored, or worn.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
1 - RETAINER CHECK BALL Clean the clutch components with solvent and dry
them with compressed air.
Check condition of the input shaft seal rings. It is
not necessary to remove or replace rings unless they
are broken, cracked, or no longer securely hooked
together.
Inspect the input shaft splines and machined surfaces.
Very minor nicks or scratches can be smoothed
off with crocus cloth. replace the shaft if the splines
are damaged, or any of the machined surfaces are
severely scored.
1 - FRONT CLUTCH RETAINER BUSHINGS (NONSERVICEABLE) Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the facing
is flaking off.
Replace the steel plates and the pressure plate if
heavily scored, warped, or broken. Be sure the driving
lugs on the discs and plates are also in good condition.
The lugs must not be bent, cracked or
damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
steel plates should slide freely in the slots. Replace
the retainer if the grooves are worn or damaged. Also
check action of the retainer check ball. The ball must
move freely and not stick.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously damaged.
Check thrust washer condition. Washer thickness
should be 1.55 to 1.60 mm (0.061 to 0.063 in.).
Replace the washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the two seal rings on the input
shaft and the single seal ring on the piston retainer
hub. Replace the seal rings only if severely worn,
cracked, or cannot be hooked together. Clean the intermediate shaft and planetary components
in solvent and dry them with compressed air.
Do not spin the planetary pinion gears with compressed
air.
Inspect the planetary gear sets and annulus gears.
The planetary pinions, shafts, washers, and retaining
pins are serviceable. However, if a pinion carrier is
damaged, the entire planetary gear set must be
replaced as an assembly.
Replace the annulus gears if the teeth are chipped,
broken, or worn, or the gear is cracked. Replace the
planetary thrust plates and the tabbed thrust washers
if cracked, scored or worn.
Inspect the machined surfaces of the output shaft.
Be sure the oil passages are open and clear. Replace
the shaft if scored, pitted, or damaged.
Inspect the sun gear and driving shell. If either
component is worn or damaged, remove the sun gear
rear retaining ring and separate the sun gear and
thrust plate from the driving shell. Then replace the
necessary component.
Replace the sun gear as an assembly if the gear
teeth are chipped or worn. Also replace the gear as
an assembly if the bushings are scored or worn. The
sun gear bushings are not serviceable. Replace the
thrust plate if worn, or severely scored. Replace the
driving shell if distorted, cracked, or damaged in any
way.
Replace all snap rings during geartrain assembly.
Reusing snap rings is not recommended.Governor and park gear
Extension housing and park lock
Valve body

Fig. 218 Governor Weights
2 - SNAP RING
3 - INNER WEIGHT
4 - INNER WEIGHT SPRING
5 - OUTER WEIGHT
Fig. 219 Governor Components
2 - SEAL RING (HOOK END)
3 - PARK GEAR
4 - GOVERNOR BODY
5 - GOVERNOR VALVE
6 - VALVE SHAFT
7 - E-CLIPS (2)
8 - FILTER
9 - SNAP RING (THIN)
10 - SNAP RING (THICK)
11 - SNAP RING
12 - RETAINER WASHER
13 - GOVERNOR WEIGHT ASSEMBLY
14 - GOVERNOR BODY BOLTS (4)
15 - WASHER
Fig. 220 Park Sprag, Shaft And Spring
2 - PARALLEL JAW SNAP RING PLIERS
3 - SPRAG
4 - SPRING
Fig. 221 Park Sprag Reaction Plug And Spring Location
2 - REACTION PLUG
Fig. 222 Correct Position Of Sprag And Spring
2 - SPRAG LOCKING LUG
3 - SPRING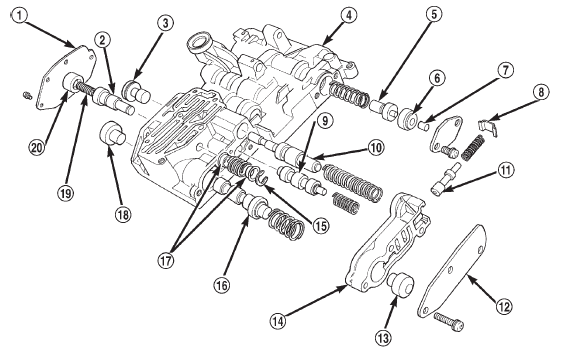
Fig. 223 Valve Body Components
2 - SHUTTLE VALVE
3 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
4 - VALVE BODY
5 - REGULATOR VALVE THROTTLE PRESSURE PLUG
6 - SLEEVE
7 - LINE PRESSURE PLUG
8 - RETAINER
9 - 1-2 SHIFT VALVE
10 - 1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE
11 - KICKDOWN LIMIT VALVE
12 - END PLATE
13 - THROTTLE PRESSURE PLUG
14 - KICKDOWN LIMIT VALVE BODY
15 - E-RING
16 - 2-3 SHIFT VALVE
17 - GUIDES
18 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
19 - PRIMARY SPRING
20 - SHUTTLE VALVE THROTTLE PLUGTransmission
Overrunning clutch/low-reverse
drum/overdrive piston retainer
Front servo

Fig. 224
2 - O-RING
3 - SNAP-RING
4 - SEAL RING
5 - PISTON ROD GUIDE
6 - SNAP-RING
7 - SERVO SPRING
8 - PISTON ROD
9 - SERVO PISTONOil pump and reaction shaft support

Fig. 225 Rear Servo Components
2 - PISTON SEAL
3 - PISTON PLUG
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - SNAP RING
6 - PISTON SPRING
7 - CUSHION SPRING
8 - PISTONFront clutch

Fig. 226 Front Clutch Piston Retainer Check Ball LocationRear clutch

Fig. 227 Retainer Bushing Location/InspectionPlanetary geartrain/output shaft
 Front clutch. Rear clutch. Planetary geartrain/output shaft
Front clutch. Rear clutch. Planetary geartrain/output shaft
Other materials:
To Resume. To Vary The Speed Setting. Setting The Following Distance In ACC
To Resume
If there is a set speed in memory push the RES (resume)
button and then remove your foot from the accelerator
pedal. The EVIC/DID will display the last set speed.
NOTE:
If your vehicle stays at standstill for longer than two
seconds, then the driver will either have to push the
...

