Jeep Cherokee (XJ): Disassembly and assembly. Cleaning and inspection. Specifications
CYLINDER BLOCK DISASSEMBLY Refer to the applicable sections for detailed
instructions.
(1) Drain the engine oil. Remove and discard the
oil filter.
(2) Remove the water pump from the cylinder
block.
(3) Remove the vibration damper.
(4) Remove the timing case cover and lay the cover
upside down.
(5) Position a drift punch into the slot in the back
of the cover and tap the old seal out.
(6) Remove the oil slinger from crankshaft.
(7) Remove the camshaft retaining bolt and
remove the sprockets and chain as an assembly.
(8) Remove the camshaft.
(9) Remove the oil pan and gasket.
(10) Remove the front and rear oil galley plugs.
(11) Remove the oil pump.
(12) Remove the connecting rods and the pistons.
Remove the connecting rod and piston assemblies
through the top of the cylinder bores.
(13) Remove the crankshaft. ASSEMBLY Refer to the applicable sections for detailed
instructions.
(1) Install the crankshaft.
(2) Install the connecting rods and the pistons
through the top of the cylinder bores.
(3) Install the oil pump.
(4) Install the oil pan and gasket.
(5) Install the camshaft.
(6) Install the sprockets and chain as an assembly.
(7) Install the oil slinger from the crankshaft.
(8) Install the timing case cover seal.
(9) Install the timing case cover.
(10) Install the vibration damper.
(11) Install the water pump. Tighten the mounting
bolts to 31 N·m (23 ft. lbs.) torque. (12) Lubricate the oil filter seal with clean engine
oil. Tighten oil filter to 18 N·m (156 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install the engine into the vehicle.
(14) Fill the engine with clean lubrication oil (refer
to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance).
(15) Fill the cooling system. CLEANING Thoroughly clean the engine cylinder head and cylinder
block mating surfaces. Clean the intake and
engine exhaust manifold and engine cylinder head
mating surfaces. Remove all gasket material and carbon.
Check to ensure that no coolant or foreign material
has fallen into the tappet bore area.
Remove the carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers and top of the pistons. INSPECTION Use a straightedge and feeler gauge to check the
flatness of the engine cylinder head and block mating
surfaces. CLEANING Remove any original sealer from the cover sealing
surface of the engine cylinder head and clean the
surface using a fabric cleaner.
Remove all residue from the sealing surface using
a clean, dry cloth. INSPECTION Inspect the engine cylinder head cover for cracks.
Replace the cover, if cracked.
The original dark grey gasket material should
NOT be removed. If sections of the gasket material
are missing or are compressed, replace the engine
cylinder head cover. However, sections with minor
damage such as small cracks, cuts or chips may be
repaired with a hand held applicator. The new material
must be smoothed over to maintain gasket
height. Allow the gasket material to cure prior to
engine cylinder head cover installation. CLEANING Clean all the components with cleaning solvent.
Use compressed air to blow out the oil passages in
the rocker arms and push rods. INSPECTION Inspect the pivot surface area of each rocker arm.
Replace any that are scuffed, pitted, cracked or
excessively worn.
Inspect the valve stem tip contact surface of each
rocker arm and replace any rocker arm that is deeply
pitted.
Inspect each push rod end for excessive wear and
replace as required. If any push rod is excessively
worn because of lack of oil, replace it and inspect the
corresponding hydraulic tappet for excessive wear.
Inspect the push rods for straightness by rolling
them on a flat surface or by shining a light between
the push rod and the flat surface.
A wear pattern along the length of the push rod is
not normal. Inspect the engine cylinder head for
obstruction if this condition exists. CLEANING Clean each tappet assembly in cleaning solvent to
remove all varnish, gum and sludge deposits. INSPECTION Inspect for indications of scuffing on the side and
base of each tappet body.
Inspect each tappet base for concave wear with a
straightedge positioned across the base. If the base is
concave, the corresponding lobe on the camshaft is
also worn. Replace the camshaft and defective tappets.
After cleaning and inspection, test each tappet for
specified leak-down rate tolerance to ensure zero-lash
operation (Fig. 84).
Swing the weighted arm of the hydraulic valve tappet
tester away from the ram of the Leak-Down
Tester.
(1) Place a 7.925-7.950 mm (0.312-0.313 inch)
diameter ball bearing on the plunger cap of the tappet.
(2) Lift the ram and position the tappet (with the
ball bearing) inside the tester cup.
(3) Lower the ram, then adjust the nose of the ram
until it contacts the ball bearing. DO NOT tighten
the hex nut on the ram.
(4) Fill the tester cup with hydraulic valve tappet
test oil until the tappet is completely submerged.
(5) Swing the weighted arm onto the push rod and
pump the tappet plunger up and down to remove air.
When the air bubbles cease, swing the weighted arm
away and allow the plunger to rise to the normal
position.
(6) Adjust the nose of the ram to align the pointer
with the SET mark on the scale of the tester and
tighten the hex nut. (7) Slowly swing the weighted arm onto the push
rod.
(8) Rotate the cup by turning the handle at the
base of the tester clockwise one revolution every 2
seconds.
(9) Observe the leak-down time interval from the
instant the pointer aligns with the START mark on
the scale until the pointer aligns with the 0.125
mark. A normally functioning tappet will require
20-110 seconds to leak-down. Discard tappets with
leak-down time interval not within this specification.
1 - POINTER CLEANING Thoroughly clean the oil pan and engine block gasket
surfaces. Use compressed air to clean out: Once the block has been completely cleaned, apply
Loctite PST pipe sealant with Teflon 592 to the
threads of the front and rear oil galley plugs. Tighten
the plugs to 34 N·m (25 ft. lbs.) torque. INSPECTION (1) It is mandatory to use a dial bore gauge to
measure each cylinder bore diameter (Fig. 85). To
correctly select the proper size piston, a cylinder bore
gauge, capable of reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.)
INCREMENTS is required. If a bore gauge is not
available, do not use an inside micrometer.
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at three levels below top of bore. Start perpendicular
(across or at 90 degrees) to the axis of the
crankshaft and then take two additional reading.
(3) Measure the cylinder bore diameter crosswise
to the cylinder block near the top of the bore. Repeat
the measurement near the middle of the bore, then
repeat the measurement near the bottom of the bore.
(4) Determine taper by subtracting the smaller
diameter from the larger diameter.
(5) Rotate measuring device 90 and repeat steps
above.
(6) Determine out-of-roundness by comparing the
difference between each measurement.
(7) If cylinder bore taper does not exceed 0.025
mm (0.001 inch) and out-of-roundness does not
exceed 0.025 mm (0.001 inch), the cylinder bore can
be honed. If the cylinder bore taper or out- of-round
condition exceeds these maximum limits, the cylinder
must be bored and then honed to accept an oversize
piston. A slight amount of taper always exists in the
cylinder bore after the engine has been in use for a
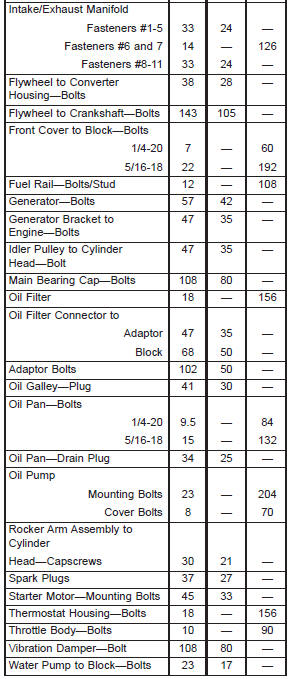
period of time. Specifications 4.0L ENGINE
Torque specifications 4.0L ENGINE
Disassembly and assembly
Cleaning and inspection
Cylinder head
Cylinder head cover
Rocker arms and push rods
Hydraulic tappets

Fig. 84 Leak-Down Tester
2 - WEIGHTED ARM
3 - RAM
4 - CUP
5 - HANDLE
6 - PUSH RODCylinder block

Fig. 85 Cylinder Bore MeasurementSpecifications








 Crankshaft oil seals-rear. Oil pump. Timing case cover oil seal
Crankshaft oil seals-rear. Oil pump. Timing case cover oil seal
Other materials:
Power steering
Description and operation
STEERING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The power steering system has a hydraulic pump.
The pump is a constant flow rate and displacement,
vane-type pump. The pump on the 4.0L engine has a
reservoir mounted to it (Fig. 1). The 2.5L engine has
a remote mounted reservoir.
The ...

